The lack of your typical CHF clinical indicators makes it difficult for CDI to put together a query. Coughing wheezing difficulty laying flat to sleep as well as an irregular heartbeat can also be symptoms.
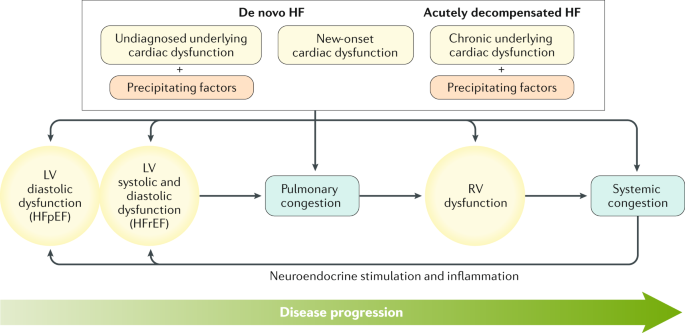 Acute Heart Failure Nature Reviews Disease Primers
Acute Heart Failure Nature Reviews Disease Primers
222 Cardiac defibrillator implant with cardiac catheterization with ami hf or shock with mcc.

Acute on chronic diastolic heart failure. There is a relative lack of data to guide medical therapy in patients with diastolic congestive heart failure especially when compared with systolic congestive heart failure. A billable code is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Systolic heart failure is characterized by ventricular dilation and reduced ejection fraction and this syndrome may be either chronic or acute.
What is Diastolic Heart Failure. Diastolic heart failure acute on chronic. If patient is Cold and Wet known by touching the legs decrease or hold Beta blocker cold and wet low perfusion and congestion are the sickest so may need ICU treatment depending on the situation.
Acute or chronic failure can begin on either the left or right side of your heart or both sides may fail at the same time. 292 Heart failure and shock with cc. ICD-10-CM I5033 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Groups MS-DRG v 380.
This leads to left ventricular hypertrophy which decreases cardiac compliance. Diastolic heart failure is also known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction HFpEF. Acute heart failure can also present with symptoms of rapid swelling and fluid retention characterized by sudden weight gain up to several pounds in a 24-hr period.
Heart failure can lead to symptoms such as trouble breathing swelling and feeling tired. Acute on chronic combined systolic congestive and diastolic congestive heart failure. The chambers where your blood is.
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I5043 became effective on October 1 2020. Treatment typically includes taking meds for symptoms. Common symptoms reported by people with chronic diastolic heart failure.
Diastolic heart failure technically referred to as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction HFpEF is a condition where the lower left chamber of the heart left ventricle is not able to fill properly with blood during the diastolic phase reducing the amount of blood pumped out to the body. Coreg or Toprol XL Start Beta Blockers at low doses and when patient is euvolemic. In some cases acute heart failure results from a sudden event such as a virus or a trauma or blockage affecting an artery around the heart.
Our device rep invited us to a webinar a year or so ago and they talked about how the TAVR itself is treatment for acute CHF. CDI does not routinely pursue acute CHF on our TAVR encounters because like you said there is typically a lack of clinical indicators. The diastolic phase is when the heart relaxes and fills with blood.
Acute heart failure resulting from cardiomyopathy has similar functional and morphologic abnormalities. According to a 2017 review roughly half of people worldwide with heart failure have diastolic. Since then our physicians do regularly document.
I5043 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. In some cases it is related to pre-existing cardiomyopathy. Left ventricular remodeling is the principal cause of progression of systolic heart failure.
I5033 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of acute on chronic diastolic congestive heart failure. The most common cause of diastolic dysfunction and failure is chronic hypertension. 291 Heart failure and shock with mcc.
The ICD code I50 is used to code Acute decompensated heart failure. Chronic diastolic heart failure is characterized by a stiffness of the left ventricle which means the heart doesnt relax and fill with blood normally. 223 Cardiac defibrillator implant with cardiac catheterization with ami hf or shock without mcc.
This is an NCLEX review for chronic bronchitis vs emphysema. In the previous review I covered other respiratory disorders.
 Lung Health Institute Difference Between Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis
Lung Health Institute Difference Between Emphysema Chronic Bronchitis
Symptoms of bronchitis come and go and are more notable.

Emphysema vs chronic bronchitis. How chronic bronchitis emphysema differ. However both conditions are chronic and the symptoms will recur at regular intervals. Emphysema chronic bronchitis together are called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
However these two conditions differ in many ways especially the pathophysiology. Chronic bronchitis is a lung condition that destroys tiny hairs called cilia in the airways of the lungs. The main difference between these conditions is that chronic bronchitis produces a frequent cough with mucus.
These air sacs supply oxygen to the blood so when they are damaged less oxygen can enter the blood. From coughing wheezing breath shortness phlegm. If youve been diagnosed with emphysema youve probably been diagnosed with chronic bronchitis as well or vice versa.
These two diseases are part of a group of disorders known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD. Both emphysema and chronic bronchitis are COPDs. Mobeen Syed explains tha.
One main difference between chronic bronchitis and emphysema is that chronic bronchitis refers to a health diagnosissomeone who has a chronic cough with mucous production every day for at least three months for two years in a row. There is a fine line between emphysema and bronchitis wrote one MyCOPDTeam member. Theyre part of a disorder known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD.
What is the difference between Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema. Emphysema affects alveoli chronic bronchitis affects bronchial tubes. Differences between emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
Advertentie Beneficial support for acute or chronic bronchitis emphysema asthma dyspnea and COPD. Decrease in gas exchange in lungs. The main symptom of emphysema is shortness of breath.
Bronchitis affects the windpipe and passageways of the lungs which become. Patients who have chronic bronchitis and emphysema struggle with shortness of breath and proper gas exchange. Both types of COPD involve changes in the lungs but the changes in bronchitis come and go while those in emphysema are permanent.
Advertentie Beneficial support for acute or chronic bronchitis emphysema asthma dyspnea and COPD. In emphysema the main problem in the air sacs. Pink skin Pursed-lip breathing.
Chronic bronchitis is considered the opposite of emphysema because instead of destruction it causes inflammation. Emphysema can sometimes arise. Although chronic bronchitis and emphysema usually occur together and may cause similar symptoms they are two distinct diseases.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are two conditions found in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD. Emphysema and chronic bronchitis are both long-term lung conditions.
Emphysema is usually present in smokers. Emphysema is a lung condition where the air sacs -- or alveoli -- become damaged. Is There a Difference.
Cyanosis due to hypoxemia. Both will present with difficulty in breathing. Because many people have both emphysema and.
Chronic Bronchitis Blue Bloater Emphysema Pink Puffer Chronic productive cough. In chronic bronchitis it is in the air tube. From coughing wheezing breath shortness phlegm.
Halaman
Renew Physical Therapy
Cari Blog Ini
Label
- 1000
- 10000
- 1500
- 2015
- 29th
- 5000
- abdominal
- ablation
- about
- acetaminophen
- acetonide
- aches
- achy
- acid
- acne
- active
- acupressure
- acupuncture
- adaptogenic
- adderall
- adhd
- admitted
- adults
- advil
- affect
- affordable
- after
- aftercare
- aggregation
- aids
- alcohol
- alcoholic
- aleve
- alienation
- allegra
- allergic
- allergies
- allergy
- allowance
- almond
- american
- aminos
- amiodarone
- anemia
- anise
- ankle
- ankles
- announce
- anorexics
- anti
- antibiotics
- anticoagulant
- antidepressants
- antigen
- anxiety
- anything
- aortic
- apathy
- apple
- arizona
- armpit
- arms
- around
- arterial
- artery
- arthritis
- ascending
- asleep
- aspergers
- assaulted
- atorvastatin
- attack
- attacks
- autism
- autoimmune
- average
- avoid
- awake
- away
- azelastine
- babassu
- babies
- baby
- babymoon
- babysit
- back
- bacterial
- bagel
- baking
- baldness
- balls
- banana
- bars
- base
- basil
- bath
- bathe
- bcaa
- beach
- beans
- beat
- beer
- before
- begin
- behind
- being
- belly
- benadryl
- bench
- benefits
- best
- between
- biceps
- bigger
- bile
- biometric
- biopsy
- bipolar
- birth
- bismol
- bite
- bites
- biting
- black
- blackhead
- bladder
- bleach
- bleeding
- blisters
- bloating
- block
- blockage
- blockers
- blood
- blue
- body
- boiled
- bone
- boneless
- bosley
- bourbon
- bowels
- brace
- bracelet
- braces
- brain
- branch
- break
- breakfast
- breakthrough
- breast
- breastfeed
- breastfeeding
- breath
- breathe
- bridge
- broken
- broth
- brown
- bruise
- bruised
- bruises
- brush
- bubble
- buck
- bugs
- building
- bulk
- bump
- bumps
- bunches
- bunion
- burger
- burn
- burner
- burning
- bursts
- busted
- butter
- caffeine
- calculator
- calorie
- calories
- cambogia
- canal
- cancer
- carb
- carbonated
- carbs
- care
- carnation
- cartilage
- cartoons
- casein
- castor
- castration
- cause
- causes
- causing
- cavities
- cavity
- cell
- cells
- cervical
- cervix
- chadwickâs
- challenge
- chamomile
- chances
- chapped
- charcoal
- check
- cheese
- chemo
- chest
- chicken
- childhood
- children
- chili
- chills
- chin
- chinese
- chipped
- chips
- chocolate
- chronic
- cider
- cigarette
- cirrhosis
- cities
- citric
- clean
- cleaning
- clear
- clinical
- clogged
- clothing
- clots
- cloudy
- coconut
- coffee
- cold
- colic
- colitis
- collar
- cologuard
- colonoscopy
- color
- coloring
- comfortable
- commit
- common
- complex
- concentrate
- conception
- concussion
- condoms
- confirm
- conjunctivitis
- cons
- consequence
- considered
- constipation
- contagious
- contrast
- control
- coolsculpting
- copd
- copper
- corn
- cornstarch
- corona
- cost
- costs
- cottage
- cough
- coughing
- count
- cover
- coverage
- covered
- cramps
- cranberry
- crawl
- cream
- creamer
- crepey
- cries
- crispy
- crown
- crying
- cucumber
- cumin
- curve
- cycle
- cyst
- cystic
- dairy
- damaged
- dandruff
- dark
- dayquil
- days
- dead
- death
- deep
- dehydration
- delt
- dentures
- depressant
- depression
- dermaroller
- description
- desserts
- detachment
- device
- diabetes
- diabetic
- diabeticorum
- diabetics
- diagnosis
- diaper
- diarrhea
- diastolic
- diatomaceous
- didnt
- diet
- diff
- difference
- diovan
- disability
- disc
- discharge
- disease
- dislodge
- disorder
- dizziness
- dizzy
- doctors
- does
- dogs
- donate
- donating
- dosage
- double
- down
- doxycycline
- drainage
- dreams
- dried
- drink
- drinking
- drinks
- drip
- drooling
- drops
- drug
- drumstick
- drunk
- dual
- duct
- dulcolax
- during
- dying
- dynamic
- dysfunction
- early
- ears
- earth
- easy
- eating
- eczema
- educational
- effects
- effexor
- eggs
- ejection
- electric
- electrolysis
- elevation
- eligibility
- elliptical
- emphysema
- endometriosis
- endurance
- energy
- enhancement
- enlarged
- enlargement
- ensure
- epilator
- epilepsy
- epipen
- epsom
- erectile
- espresso
- essential
- estrogen
- eucalyptus
- every
- exactly
- excedrin
- excessive
- exercise
- exercises
- expectancy
- extensions
- extenze
- extraction
- eyeball
- eyebrows
- eyed
- eyelash
- eyelid
- eyelids
- eyes
- face
- facelifts
- facts
- failure
- fake
- fall
- fast
- faster
- fathers
- fatigue
- features
- feed
- feel
- feeling
- feet
- female
- fertility
- fetal
- fever
- fiberglass
- fibroglandular
- fibroids
- fibromyalgia
- fibrosis
- fillers
- fills
- finger
- fingertip
- first
- fish
- fixing
- flapping
- flashes
- flea
- fleas
- flipper
- floor
- flour
- fluocinolone
- fluoride
- foam
- food
- foods
- foot
- forearm
- forehead
- forhead
- formula
- fraction
- freckles
- free
- freeze
- fridge
- fried
- from
- front
- frozen
- fruit
- fungus
- gain
- gainer
- gallon
- games
- garcinia
- garden
- gastritis
- gear
- gender
- generic
- gerd
- germ
- getting
- giant
- gifts
- ginger
- give
- giving
- glass
- gluten
- glycol
- good
- grade
- greasy
- green
- greenish
- grow
- growth
- gummy
- gums
- guys
- hair
- hairline
- hand
- hands
- happens
- hard
- have
- hctz
- head
- headache
- headaches
- headed
- heal
- healed
- healing
- health
- healthiest
- healthy
- Healtline
- hearing
- heart
- heartburn
- heat
- heavy
- heel
- helmets
- help
- hemorrhoids
- henna
- herbs
- hernia
- herniated
- herpes
- high
- hips
- hives
- hold
- holy
- home
- homemade
- homeopathic
- honey
- honeycrisp
- hormonal
- hormone
- hormones
- hospital
- hour
- human
- hurt
- hurts
- hyclate
- hydrochlorothiazide
- hydrocodone
- hydrogen
- hydromorphone
- hydroxycut
- hyperpigmentation
- identical
- idiopathic
- impingement
- implant
- implants
- impotent
- incontinence
- increase
- induce
- induced
- infarction
- infection
- infections
- inflammatory
- info
- information
- ingredient
- ingrown
- inguinal
- inhaler
- injection
- injections
- inner
- insertion
- instant
- instead
- insurance
- internal
- into
- intolerance
- invasive
- invisalign
- iron
- irregular
- isolate
- itching
- itself
- jacket
- jade
- jelly
- jerky
- joint
- juice
- juicing
- just
- juvederm
- kamut
- karo
- keep
- keflex
- keto
- kick
- kidney
- kids
- kill
- killing
- king
- kiwi
- knee
- krispies
- labor
- lactose
- laser
- last
- late
- lead
- leak
- leaky
- learn
- left
- legs
- lemonade
- lesion
- levothyroxin
- lexapro
- lice
- life
- lift
- ligation
- light
- like
- lime
- lipitor
- liposuction
- lipotropic
- lips
- lipstick
- lisinopril
- list
- live
- liver
- living
- lobster
- long
- loose
- losartan
- lose
- loss
- lower
- lumineers
- lump
- lumps
- lunch
- lung
- lying
- lymph
- lymphoma
- macaroni
- made
- make
- making
- male
- many
- mark
- mask
- mass
- massage
- massager
- mattresses
- maximum
- mayo
- mayonnaise
- mcdonalds
- meal
- meals
- mean
- meaning
- meat
- mederma
- medicare
- medication
- medications
- medicine
- meningitis
- meniscus
- menopause
- metabolism
- metastatic
- metformin
- methicillin
- micro
- microblading
- micropigmentation
- middle
- migraine
- migraines
- milk
- minoxidil
- miracle
- miralax
- mirena
- miscarriage
- miso
- missed
- missing
- moisturizer
- mole
- moles
- mons
- month
- months
- morning
- mortality
- mosquito
- most
- mountain
- mouth
- moving
- mozzarella
- much
- mucinex
- mucus
- multiple
- muscle
- muscular
- mushroom
- myocardial
- myself
- nail
- nails
- narcissist
- nasal
- natural
- naturally
- nausea
- near
- neck
- need
- needling
- negative
- nerve
- nerves
- neuropathy
- newborn
- newborns
- nicotine
- night
- nightmares
- nodal
- nodes
- noodles
- normal
- nose
- novolin
- novolog
- nsaids
- numb
- nutrition
- nuts
- nyquil
- oatmeal
- oats
- oblique
- obstruction
- ocean
- often
- oils
- olive
- onion
- open
- opioid
- optimum
- oral
- orange
- origin
- ortho
- osteoarthritis
- outbreak
- outer
- ovarian
- over
- overdose
- ovulating
- oximetry
- pack
- pain
- palmar
- palmetto
- palms
- palpitation
- pancreas
- pancreatic
- papillomavirus
- para
- parental
- parents
- part
- pasta
- patch
- pattern
- pcos
- peanut
- peas
- peeling
- pelvis
- penile
- people
- peppermint
- percocet
- period
- periodontal
- periods
- peroxide
- person
- personality
- peyronies
- phase
- photos
- physical
- pictures
- piercing
- pill
- pillow
- pillows
- pills
- pilonidal
- pimple
- pimples
- pinched
- pineapple
- pink
- plan
- plans
- plantar
- plasma
- plateau
- platelet
- plug
- plugs
- plum
- plus
- pneumonia
- point
- points
- polish
- polyps
- popping
- popular
- pore
- pose
- poses
- position
- possible
- post
- postpartum
- postures
- potassium
- potato
- pound
- pounds
- powder
- powders
- precautions
- prednisone
- pregnancy
- pregnant
- preparation
- presion
- pressure
- preterm
- pretzel
- prevent
- primary
- prince
- proactive
- probiotic
- probiotics
- procardia
- prognosis
- progressive
- propylene
- pros
- protein
- prozac
- psoriasis
- psoriatic
- pubis
- pudding
- pull
- pulled
- pulling
- pulmonary
- pulse
- purified
- qtips
- quick
- quickly
- quinoa
- quitting
- radiating
- ramen
- rapid
- rash
- rashes
- rate
- rates
- rating
- razor
- reaction
- reactive
- rear
- recipe
- recipes
- recover
- recovery
- reduction
- relationship
- relief
- relieve
- remedies
- remedy
- remission
- removal
- remove
- remover
- removing
- renal
- replace
- replacement
- report
- requip
- resistant
- rest
- restaurants
- results
- retainer
- retainers
- reuse
- reversal
- reverse
- review
- reviews
- rheumatoid
- rice
- right
- rinds
- ringing
- risk
- roll
- rolling
- roof
- room
- root
- round
- runners
- running
- safe
- safflower
- saline
- salt
- salts
- sandwich
- save
- scabies
- scale
- scalp
- scan
- scar
- scarring
- scars
- schedule
- schizophrenia
- sclerosis
- scotch
- screening
- sedation
- seeds
- seizure
- sensation
- sensitive
- sensory
- sentence
- septoplasty
- seroquel
- sesame
- sexually
- shaft
- shakes
- sharing
- shave
- shaving
- sheets
- shingles
- shorten
- shortness
- shot
- should
- shoulder
- show
- showing
- shrink
- sick
- sickness
- side
- sign
- signs
- silica
- silicone
- sinus
- sinusitis
- sitting
- size
- skimmed
- skin
- skittles
- skunk
- skyla
- sleep
- sleeping
- sleepy
- small
- smear
- smell
- smells
- smile
- smiling
- smoke
- smoking
- snack
- snap
- snoring
- soap
- soaps
- soba
- sober
- soda
- sodium
- soles
- solids
- solution
- someone
- sonogram
- soon
- sore
- sores
- soup
- sour
- specialist
- specific
- spermicide
- spider
- spinach
- spine
- spit
- splenda
- splinters
- spot
- spots
- spotting
- sprain
- spray
- spread
- stack
- stage
- stages
- stannous
- staphylococcus
- star
- start
- started
- stay
- stds
- steel
- stem
- stenosis
- stevia
- stimulant
- sting
- stings
- stinks
- stitches
- stomach
- stone
- stones
- stool
- stools
- stop
- stopping
- stories
- straight
- strap
- stream
- strength
- strengthening
- strep
- stress
- stretch
- stretches
- strongest
- stuck
- substitute
- subways
- sudafed
- sugar
- sulfa
- sunburn
- supplement
- supplements
- supported
- supposed
- surfaces
- surgery
- surgical
- survival
- swallowing
- sweating
- swedish
- sweet
- swelling
- swimming
- swings
- swiss
- swollen
- symptom
- symptoms
- syrup
- system
- tablespoon
- tags
- tail
- take
- tamanu
- tampon
- tampons
- tansy
- tape
- taping
- taste
- tattoo
- tears
- teen
- teeth
- teething
- tell
- temporary
- tendonitis
- tenodesis
- terbutaline
- term
- terrors
- test
- testicular
- testing
- testis
- testosterone
- tests
- that
- therapy
- thick
- thicker
- thigh
- thighs
- thinners
- third
- throat
- throats
- throbbing
- thrombosis
- throw
- throwing
- thumb
- thyme
- tibial
- ticks
- tied
- tight
- tightness
- time
- timeline
- tired
- tissue
- toddlers
- toenail
- toenails
- tongue
- tonsil
- tonsillectomy
- tonsillitis
- tooth
- toothache
- toothpaste
- topamax
- topical
- torn
- tortilla
- tract
- transplant
- tratamiento
- trazodone
- treat
- treatment
- treatments
- treats
- tree
- trigger
- trimester
- triplet
- truth
- tuck
- tummy
- tuna
- turbinate
- turkey
- twins
- tylenol
- type
- ulcerative
- ultra
- ultrasound
- umbilical
- under
- underwear
- undigested
- unisom
- units
- untreated
- upper
- urinary
- urine
- uterus
- vaccine
- vaginal
- valtrex
- valve
- vapor
- variability
- varicose
- vasectomy
- vegan
- vegans
- vegetable
- vein
- veins
- veneer
- veslcare
- viagra
- vinegar
- vision
- vitals
- vitamin
- vitamins
- vyvanse
- waist
- walk
- wall
- want
- wart
- warts
- wash
- water
- waxing
- ways
- weakness
- wear
- weed
- week
- weeks
- weight
- wendys
- what
- whats
- wheat
- when
- where
- whey
- which
- while
- whip
- whipped
- whipping
- whiskey
- white
- whole
- wild
- will
- wine
- wipe
- wisdom
- with
- within
- without
- women
- womens
- wont
- work
- working
- workout
- works
- worst
- wrinkles
- yawn
- year
- years
- yeast
- yellow
- yoga
- yogurt
- your
- yourself
- zone
- zyrtec
- zzzquil
